Ah, leg day. Everyone’s favourite!
Lunges and Bulgarian split squats are two of the best exercises to target your leg muscles individually. Both exercises offer several benefits to individuals, of all levels in their fitness journey.
In this article we discuss Lunges vs Bulgarian Split Squats, helping you decide which exercise is more suited to you, or if you should include both within your workout routine.
What are the similarities?
Lunges and Bulgarian split squats are both lower-body strength exercises that target similar muscle groups.
They share several similarities:
- Primary Muscle Engagement: Both exercises primarily target the quadriceps (front thigh muscles) and the glutes (buttocks), making them effective for developing leg strength and muscle.
- Stability and Balance: Lunges and Bulgarian split squats require a significant amount of stability and balance because they are unilateral (one-leg) exercises. They engage the core and various stabilizer muscles to maintain balance.
- Versatility: Lunges and Bulgarian split squats can be adapted and modified to target different areas of the leg, depending on your stance, foot placement, and the position of your body.
- Range of Motion: Both exercises involve a similar range of motion, with the front knee flexing and extending during the movement. This allows for a full extension of the hip and knee joint during the concentric (lifting) phase.
- Functional Movement: These exercises mimic functional movements like stepping and walking, making them useful for improving everyday activities and sports performance.
- Flexibility: Lunges and Bulgarian split squats can contribute to improved flexibility in the hip flexors, hamstrings, and quadriceps due to the dynamic nature of the movements.
- Lower Back Safety: Both exercises are generally considered safe for the lower back because they don’t place excessive stress on the lumbar spine, as long as proper form is maintained.
- Progression: You can adjust the difficulty and intensity of these exercises by increasing the weight (using dumbbells, barbells, or other resistance), varying your stance, or changing the range of motion.
Both exercises are great for a lower-body workout routine, with the choice between them depending on individual preferences and training goals.
What are the differences?
While lunges and Bulgarian split squats have these similarities, they also have some key differences. The differences in technique and body positioning can lead to variations in muscle engagement and balance requirements.
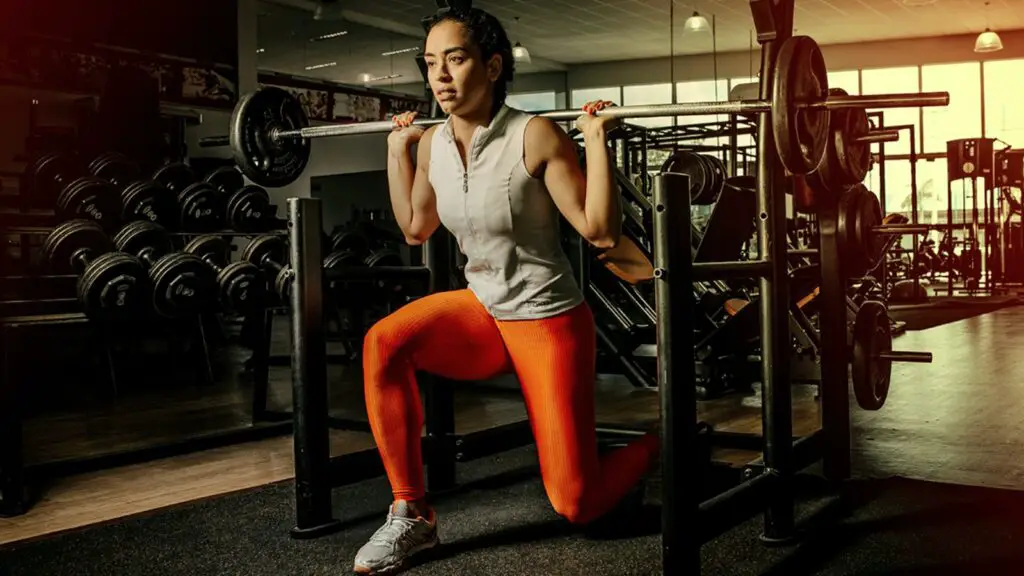

Here are the main differences between the two:
Leg Position
- Lunges: In a lunge, you typically take a step forward or backward, creating a dynamic movement. One leg is in front, and the other is behind.
- Bulgarian Split Squats: In a Bulgarian split squat, one foot is placed behind you on a bench or raised platform, and the other foot is in front. The back foot remains stationary throughout the exercise.
Range of Motion
- Lunges: Lunges often involve a more extended range of motion because you step forward or backward and return to the starting position in each repetition.
- Bulgarian Split Squats: In Bulgarian split squats, the range of motion is somewhat limited compared to lunges because the back foot remains in place, making it a more isolated, up-and-down movement.
Balance and Stability
- Lunges: Lunges require a degree of balance and coordination, but they may not be as demanding in terms of balance as Bulgarian split squats.
- Bulgarian Split Squats: Bulgarian split squats are a more stability-focused exercise. The rear foot elevation challenges balance and activates the stabilizer muscles more intensively.
Muscle Engagement
- Lunges: Lunges engage the quadriceps (front thigh muscles), glutes, hamstrings, and calf muscles. The dynamic nature of the movement involves a push-off from the back leg.
- Bulgarian Split Squats: Bulgarian split squats primarily target the quadriceps and glutes, with a greater focus on these muscle groups due to the stationary stance. The hamstrings and calves are also engaged to a lesser extent.
Impact on Back Knee
- Lunges: In lunges, the knee of the back leg often touches or hovers just above the ground during the movement, which can be more demanding on the back knee.
- Bulgarian Split Squats: In Bulgarian split squats, the back knee remains elevated and doesn’t come into contact with the ground, reducing stress on the knee.
Ease of Set-Up
- Lunges: Lunges require no additional equipment, making them easy to perform anywhere.
- Bulgarian Split Squats: Bulgarian split squats involve elevating one foot, which requires access to a bench, step, or platform.
Both exercises offer various ways to modify and progress, such as adding weights, using different stances, or changing the direction of movement. However, lunges provide more opportunities for lateral and multidirectional variations.
The primary difference is that in lunges, you step forward or backward and return to the starting position, while in Bulgarian split squats, one foot is elevated behind you, and you perform the exercise with a stationary stance.
The differences in technique and body positioning can lead to variations in muscle engagement and balance requirements.
Target muscle
Lunges and Bulgarian split squats target similar muscle groups in the lower body, but they engage these muscles differently due to the variations in the exercises.
Here are the primary target muscles for both lunges and Bulgarian split squats:
Lunges
- Quadriceps (Front Thigh Muscles): Lunges place significant emphasis on the quadriceps, especially the rectus femoris, which is one of the four muscles of the quadriceps group.
- Gluteus Maximus (Glutes): Lunges engage the glutes to a substantial degree, contributing to improved strength and shape in the buttocks.
- Hamstrings (Back of Thighs): While not the primary target, lunges also work the hamstrings to some extent, helping balance leg development.
- Calves (Gastrocnemius and Soleus): The calf muscles assist in providing stability and propulsion during the lunge movement.
- Hip Adductors: The hip adductors, inner thigh muscles, help stabilize the hips during the lunge.
Bulgarian Split Squats
- Quadriceps (Front Thigh Muscles): Bulgarian split squats place a significant focus on the quadriceps, making them a highly effective exercise for leg strength and development.
- Gluteus Maximus (Glutes): The glutes are heavily engaged in Bulgarian split squats, contributing to improved hip strength and shaping the buttocks.
- Adductors (Inner Thigh Muscles): The adductor muscles are actively involved in maintaining hip and knee stability, especially when performing Bulgarian split squats.
- Hamstrings (Back of Thighs): Although the hamstrings play a secondary role, they assist in the overall stability and control of the movement.
- Hip Flexors (Iliopsoas): The hip flexors are engaged to stabilize the hip joint during the exercise.
- Calves (Gastrocnemius and Soleus): As in lunges, the calf muscles provide stability and support.
Both exercises are effective for building lower body strength and muscle.
The choice between lunges and Bulgarian split squats may depend on individual goals, equipment availability, and preference for dynamic movement versus stability-focused exercises.
Incorporating both exercises into your leg training routine can help ensure balanced lower body development.
How to do Lunges?
Lunges help build strength and muscle in the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes while also engaging the calf muscles and improving balance.
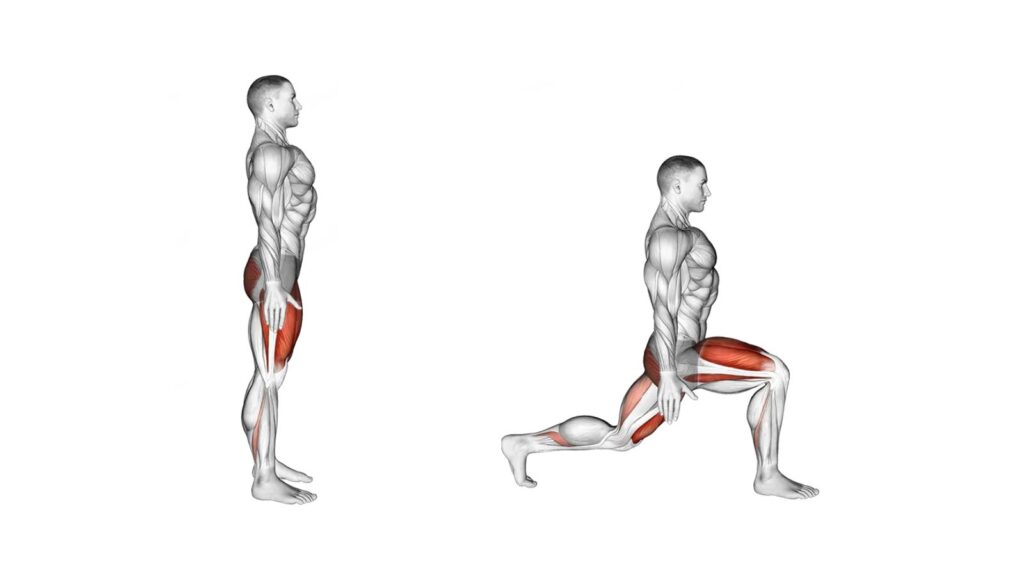
Here’s how to perform a basic lunge without weight:
- Starting Position:
- Stand up straight with your feet hip-width apart. Keep your core engaged for stability.
- Take a Step Forward:
- Decide which leg you want to start with. In this example, let’s begin with the right leg. Take a step forward with your right leg. Your left leg should remain in place.
- Your feet should be about shoulder-width apart or slightly wider.
- Lunge Down:
- Lower your body by bending both knees. As you descend, aim to create two 90-degree angles with your legs. Your front knee should be directly above your ankle, and your back knee should hover just above the ground without touching it.
- Keep your torso upright and avoid leaning forward. Look straight ahead.
- Pause and Engage Muscles:
- Hold the lunge position for a brief moment to engage the target muscles (quads, hamstrings, and glutes).
- Push Back Up:
- Push off your front foot to return to the starting position. Use your front leg to drive the movement.
- Exhale as you push up.
- Repeat on the Other Leg:
- After completing the desired number of repetitions on one leg, switch to the other leg and perform lunges with the opposite leg forward.
Tips for a Safe and Effective Lunge:
- Keep your movements controlled and avoid rushing through the exercise to maintain proper form.
- Maintain a neutral spine and keep your back straight throughout the movement.
- Ensure that your front knee is aligned with your ankle and does not go past your toes.
- Use your core muscles for balance and stability.
- Keep your chest up and your gaze forward to maintain good posture.
- For added resistance, you can hold dumbbells or a barbell in your hands. Alternatively, you can use a weighted vest.
Lunges can be performed in various ways, including reverse lunges (stepping backward), walking lunges (moving forward with each step), and lateral lunges (stepping to the side).
Incorporating different lunge variations can add variety to your lower body workouts and target the muscles from various angles.
When should you do Lunges?
The timing for when to do lunges can vary based on your overall workout routine and fitness goals.
Here are some common scenarios for incorporating lunges into your training schedule:
- Leg Day: Lunges are often included as part of a dedicated leg training day. On leg day, you can perform various lower body exercises to target the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes.
- Full-Body Workouts: If you follow a full-body workout routine, you can include lunges in your workouts that involve a combination of upper body and lower body exercises.
- Warm-Up or Mobility Routine: Lunges can serve as a dynamic warm-up exercise to prepare your muscles and joints for more intense physical activity. They can also be included in a mobility routine to improve hip flexibility and balance.
- Cardio Workouts: Lunges can be incorporated into cardio workouts as a way to increase intensity and build strength while performing bodyweight or walking lunges.
- Functional Training: Lunges are useful for functional training, helping improve stability and balance, which can be beneficial for daily activities and sports performance.
- Accessory Exercise: Lunges can be used as an accessory exercise to complement primary lower body exercises like squats or deadlifts. They can help address muscle imbalances and provide variety in your training.
- Rehabilitation: In some cases, lunges can be part of a rehabilitation program for individuals recovering from knee or hip injuries. However, it’s essential to consult with a physical therapist for guidance in such situations.
- Strength and Muscle Building: Lunges can be incorporated into a program focused on building leg strength and muscle. Variations of lunges, such as walking lunges, Bulgarian split squats, or reverse lunges, can be used to target specific muscle groups.
Whether you’re looking to build strength, improve balance, or enhance your lower body muscle development, lunges can be a valuable addition to your fitness routine.
Benefits of Lunges
Lunges are a versatile lower body exercise that offers a wide range of benefits for individuals looking to build leg strength, improve balance, and enhance their overall fitness.
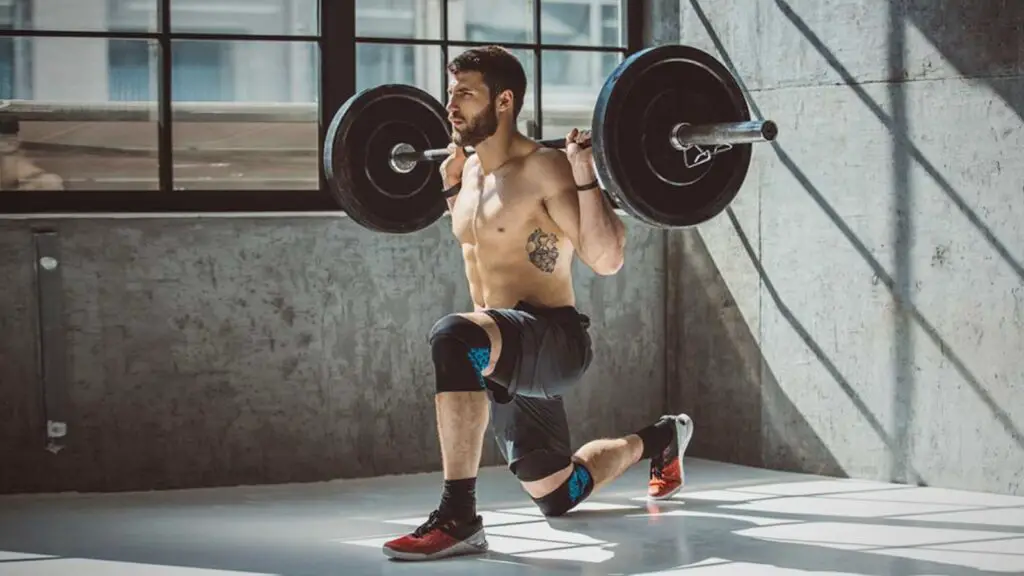

Here are some of the key benefits of incorporating lunges into your workout routine:
- Leg Strength: Lunges target the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes, making them an effective exercise for building strength in the lower body.
- Muscle Development: Lunges help increase muscle size and definition in the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes, contributing to a toned and sculpted lower body.
- Balance and Stability: Lunges are unilateral (one-leg) exercises, which require balance and stability. Regular practice can improve your balance and coordination.
- Functional Movement: Lunges mimic common movements such as walking and climbing stairs, making them relevant for everyday activities and improving functional fitness.
- Core Engagement: To maintain balance during lunges, your core muscles are actively engaged, which can contribute to improved core strength.
- Flexibility: Lunges involve a dynamic stretch in the hip flexors, which can help improve hip flexibility and reduce the risk of tight hip muscles.
- Variety: There are various lunge variations, including walking lunges, reverse lunges, lateral lunges, and curtsy lunges, which allow you to target different leg muscles and add variety to your workouts.
- Cardiovascular Benefits: When performed with intensity, lunges can increase your heart rate and provide a cardiovascular workout in addition to their strength and muscle-building benefits.
- Injury Prevention: By strengthening the muscles around the knee and hip joints, lunges can contribute to injury prevention, especially in the context of sports and other physical activities.
- Posture Improvement: Lunges can help strengthen the muscles that support good posture, reducing the risk of slouching and poor alignment.
- Minimal Equipment: Lunges can be done with little to no equipment, making them accessible for most people and suitable for home workouts.
To maximize the benefits of lunges, ensure you perform lunges with proper form and gradually increase the difficulty or resistance to challenge your muscles and promote progress.
Cons of Lunges
While lunges offer numerous benefits, there are some potential drawbacks and limitations to consider.
It’s essential to be aware of these cons and take appropriate precautions when incorporating lunges into your fitness routine:
- Knee Strain: Lunges can place stress on the knees, particularly if performed with poor form or excessively deep range of motion. Individuals with preexisting knee issues or injuries should approach lunges with caution.
- Balance and Stability Challenges: Lunges require balance and stability, which can be challenging for beginners or individuals with balance issues. Falling or losing balance during a lunge can result in injuries.
- Hip Flexor Strain: The hip flexors can become tight or strained when performing lunges, especially if the quadriceps are significantly stronger than the hip flexors. This can lead to muscle imbalances and discomfort.
- Overuse Injuries: Excessive repetition of lunges without adequate variation or rest can lead to overuse injuries in the quadriceps or hamstrings.
- Reduced Range of Motion: Some individuals may find it difficult to achieve a deep range of motion in lunges due to flexibility limitations or joint issues, which can limit the effectiveness of the exercise.
- Lower Back Stress: Lunges can place stress on the lower back if performed with improper form. Maintaining a neutral spine and avoiding excessive forward leaning is crucial for lower back safety.
- Impact on Ankles: Lunges can place strain on the ankle joints, especially when the front knee extends beyond the toes. Individuals with ankle issues should be cautious.
- Equipment Dependency: Although lunges can be done without equipment, adding resistance (e.g., dumbbells or a barbell) may require access to additional gear, which might not be readily available in all workout environments.
- Specificity: Lunges primarily target the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes. While they offer significant benefits for these muscle groups, they may not fully engage other leg muscles.
To mitigate the cons of lunges and maximize their benefits, it’s important to prioritize safety and proper technique. Here are some tips:
- Start with bodyweight lunges and gradually add resistance as your strength improves.
- Focus on maintaining a neutral spine and proper knee alignment during the exercise.
- Incorporate a variety of lunge variations into your routine to target different leg muscles.
- If you have existing injuries or physical limitations, consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist to determine if lunges are suitable for your condition.
Like any exercise, lunges should be performed with mindfulness and consideration of individual fitness levels and limitations.
How to do Bulgarian Split Squats?
Bulgarian split squats, also known as just “Bulgarian squats,” are a challenging lower body exercise that targets the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes.
They are a variation of squats, that can provide great effectiveness when building leg muscles.
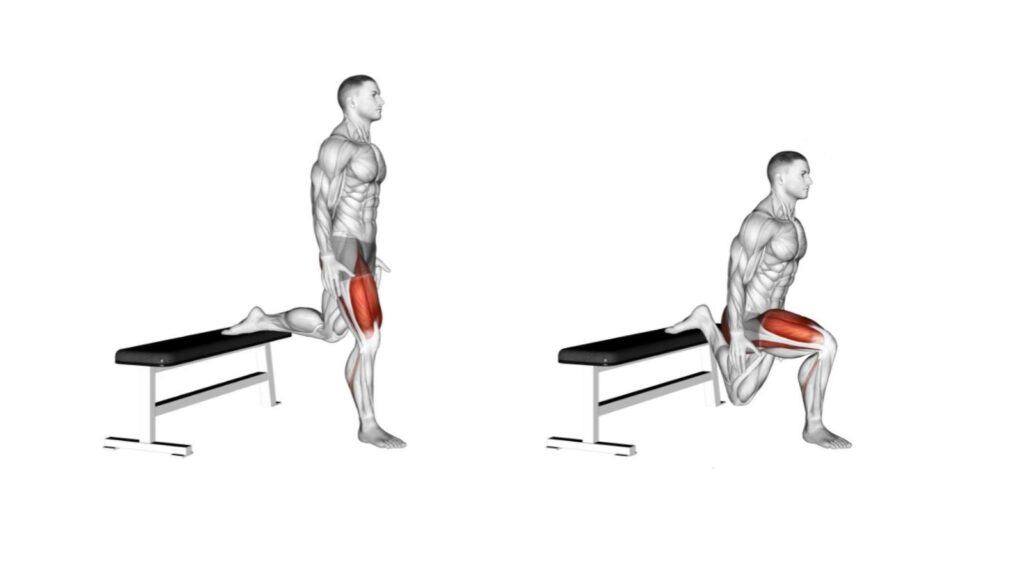
Here’s how to perform Bulgarian split squats:
- Set Up:
- Position a bench or a sturdy elevated surface a few feet behind you. You can also use a step platform or any solid surface that provides enough height.
- Stand facing away from the bench or elevated surface with your feet together.
- Lunge Position:
- Take a step forward with one foot and place the top of your rear foot (toes or the ball of your foot) on the bench or elevated surface behind you. Your feet should be hip-width apart.
- The front foot should be far enough forward that, when you lower yourself into the squat, your front knee remains directly above your front ankle, forming a 90-degree angle.
- Your back foot should be positioned on its toes, and the top of your foot should be resting on the bench.
- Posture:
- Keep your chest up, shoulders back, and your core engaged to maintain proper posture.
- Maintain a neutral spine with your head facing forward.
- Descend Into the Squat:
- Lower your body by bending your front knee, allowing your rear knee to move downward toward the ground.
- Keep your front knee aligned with your ankle, and aim to create a 90-degree angle with your front thigh parallel to the ground.
- Ensure your rear knee hovers just above the ground without touching it.
- Pause and Engage Muscles:
- Hold the squat position briefly to engage the muscles in your front leg.
- Keep your chest up, and maintain balance and control.
- Rise Back Up:
- Push through your front heel to return to the starting position. Exhale as you push up.
- Straighten your front leg completely while maintaining proper form.
- Repeat on the Other Leg:
- After completing the desired number of repetitions on one leg, switch to the other leg and perform Bulgarian split squats with the opposite leg forward.
Tips for Safe and Effective Bulgarian Split Squats:
- Focus on maintaining balance and control throughout the movement.
- Start with bodyweight Bulgarian split squats to master the form before adding weights or resistance.
- Keep your rear foot on the bench stable and avoid letting it slip or move.
- Use a controlled tempo, avoiding any jerky movements.
- Perform an equal number of repetitions on both legs to maintain muscle balance.
Bulgarian split squats can be a challenging exercise, so it’s important to use proper form and technique to prevent injury.
As you progress, you can add dumbbells or a barbell to increase the resistance and intensity of the exercise.
When should you do Bulgarian Split Squats?
When to do Bulgarian split squats varies based on your workout routine and training goals.
Here are some common scenarios for when to add it to your training schedule:
- Leg Day: Bulgarian split squats can be a central exercise on a dedicated leg training day. When you focus on training your lower body, you can perform Bulgarian split squats to target the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes effectively.
- Lower Body Split: If you follow a split routine that separates upper body and lower body workouts, Bulgarian split squats can be included on a lower body training day along with other leg exercises like squats, deadlifts, or lunges.
- Strength Training: Bulgarian split squats can be included in a strength training routine. You can use heavy weights and low repetitions to build strength in the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes.
- Muscle Hypertrophy: If your goal is muscle hypertrophy (building larger muscles), you can incorporate Bulgarian split squats into a bodybuilding-style workout. Use moderate weights and higher repetitions to stimulate muscle growth.
- Unilateral Training: Bulgarian split squats are a unilateral exercise, making them suitable for routines that focus on balancing muscle development and addressing any strength imbalances between your legs.
- Functional Training: The exercise is useful for functional training programs aimed at improving stability, balance, and lower body strength for daily activities and sports performance.
- Rehabilitation: In some cases, physical therapists may include Bulgarian split squats in rehabilitation programs for individuals recovering from knee or hip injuries.
- Accessory Exercise: Bulgarian split squats can be used as an accessory exercise to complement other primary leg exercises in your workout routine.
- Variation and Periodization: Including Bulgarian split squats as part of a periodization plan can help add variety to your training and prevent plateaus.
Bulgarian squats can be highly effective when done correctly, with the right approach. The structure of your workout is important when deciding on what exercises to do.
Benefits of Bulgarian Split Squats
Bulgarian split squats offer a variety of benefits for individuals looking to build strength and enhance their overall fitness.
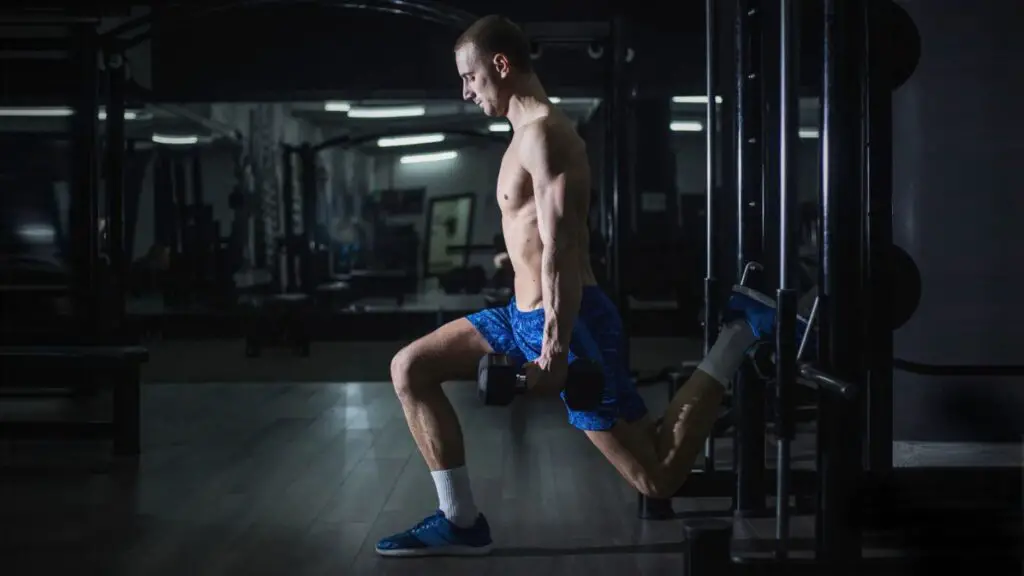

Here are some of the key benefits of Bulgarian split squats:
- Quadriceps Development: Bulgarian split squats are highly effective at targeting and building the quadriceps (front thigh muscles), contributing to improved leg strength and muscle definition.
- Glute Activation: This exercise engages the gluteus maximus (the largest muscle in the buttocks), leading to enhanced hip strength and shaping of the glutes.
- Hamstring Engagement: While the primary focus is on the quadriceps and glutes, Bulgarian split squats also work the hamstrings to a significant extent, contributing to balanced leg development.
- Unilateral Strength: Because Bulgarian split squats are a unilateral (one-leg) exercise, they help address muscle imbalances between the legs and improve overall leg strength and stability.
- Balance and Stability: The exercise requires a high degree of balance and stability due to the elevated rear foot. Regular practice can lead to improved balance and coordination.
- Functional Movement: The movement pattern of Bulgarian split squats mimics activities like walking and climbing stairs, making it relevant for daily life and improving functional fitness.
- Core Activation: To maintain balance during the exercise, your core muscles are actively engaged, leading to improved core strength.
- Hip Flexor Flexibility: The dynamic nature of the movement can help improve hip flexor flexibility, which can be beneficial for individuals with tight hip muscles.
- Variety of Progressions: You can easily adjust the difficulty of Bulgarian split squats by adding weights (dumbbells or a barbell), increasing the range of motion, or incorporating other variations.
- Lower Back Safety: Bulgarian split squats are considered safe for the lower back because they do not place excessive stress on the lumbar spine.
- Minimal Equipment: You only need an elevated surface (bench, step, or platform) to perform Bulgarian split squats, making them accessible for most people and suitable for home workouts.
- Muscle Isolation: By focusing on one leg at a time, you can isolate and target the muscles of the working leg effectively.
To fully realize these benefits, it’s important to perform Bulgarian split squats with proper form, gradually increase resistance or weights, and incorporate a variety of leg exercises into your training routine.
Cons of Bulgarian Split Squats
While Bulgarian split squats offer several advantages, there are also potential drawbacks and limitations to consider.
It’s essential to be aware of these cons and take appropriate precautions when incorporating Bulgarian split squats into your fitness routine:
- Balance and Stability Challenges: Bulgarian split squats require a high level of balance and stability, which can be challenging for beginners or individuals with balance issues.
- Knee Strain: Like any squatting movement, Bulgarian split squats can place stress on the knees, especially if performed with poor form or an excessively deep range of motion. Individuals with pre-existing knee issues or injuries should approach this exercise with caution.
- Overuse Injuries: Excessive repetition of Bulgarian split squats without adequate variation or rest can lead to overuse injuries in the quadriceps, hamstrings, or glutes.
- Flexibility Limitations: Some individuals may find it challenging to achieve a deep range of motion in Bulgarian split squats due to flexibility limitations or joint issues, which can limit the effectiveness of the exercise.
- Unilateral Focus: While the unilateral nature of the exercise helps address muscle imbalances, it may also lead to fatigue and potential overuse of the supporting leg if not balanced with other exercises.
- Hip Flexor Strain: The dynamic nature of the movement can place stress on the hip flexors, which can lead to muscle imbalances or discomfort if the quadriceps are significantly stronger than the hip flexors.
- Equipment Dependency: Bulgarian split squats require an elevated surface (bench or platform), which may not be available in all workout environments.
- Specificity: Bulgarian split squats primarily target the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes. While they offer significant benefits for these muscle groups, they may not fully engage other leg muscles.
To mitigate the cons of Bulgarian split squats and maximize their benefits, it’s important to prioritize safety and proper technique:
- Start with bodyweight Bulgarian split squats to master the form before adding weights or resistance.
- Focus on maintaining balance and control throughout the movement.
- Keep your rear foot on the bench stable and avoid letting it slip or move.
- Use a controlled tempo, avoiding any jerky movements.
- Incorporate a variety of leg exercises into your routine to provide balanced muscle development and prevent overuse injuries.
Like any exercise, Bulgarian split squats should be performed with mindfulness and consideration of individual fitness levels and limitations.
FAQs
Are lunges and Bulgarian split squats suitable for beginners?
Yes, both lunges and Bulgarian split squats can be modified to accommodate beginners.
It is important to start with proper form, use lighter weights, and gradually increase intensity as you gain strength and confidence.
Consulting with a fitness professional can also help ensure proper technique and minimize the risk of injury.
Which exercise is better for targeting the glutes?
Both exercises effectively target the glutes.
However, Bulgarian split squats tend to place more emphasis on the glute muscles due to the split stance and increased range of motion.
If glute development is a primary goal, incorporating Bulgarian split squats into your routine may be beneficial.
You can also check out our article on Squats vs Lunges, to get a better understanding on the effectiveness of squats.
Can lunges and Bulgarian split squats be done without weights?
Yes, lunges and Bulgarian split squats can be performed without weights, making them accessible for individuals who prefer bodyweight exercises or do not have access to equipment.
Bodyweight lunges and split squats still provide significant benefits and can be modified by adjusting the range of motion or incorporating additional balance challenges.
Can lunges and Bulgarian split squats help with improving sports performance?
Absolutely! Both lunges and Bulgarian split squats are functional exercises that translate well to various sports and activities.
By targeting the lower body muscles, improving strength, stability, and coordination, these exercises can enhance athletic performance, agility, and power in activities such as running, jumping, and change of direction movements.



